Which PoE Standard to Use, 802.3at vs. 802.3af?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) standards play a crucial role in determining the power delivery capabilities of network devices. Two prominent standards, IEEE 802.3at (PoE+) and IEEE 802.3af (PoE), are widely adopted, each with its own set of specifications and use cases. Understanding the differences between 802.3at and 802.3af is essential for making informed decisions in network deployments.

IEEE 802.3at (PoE+)
- Power Level: IEEE 802.3at, also known as PoE+, provides a higher power budget compared to 802.3af.
- Power Delivery: It supports a maximum power delivery of up to 25.5 watts per port.
- Applications: PoE+ is suitable for devices with higher power requirements, including advanced IP cameras, Wi-Fi access points, and certain VoIP phones.
Benefits:
- High-Power Devices: PoE+ is designed to meet the power demands of devices requiring more than 15.4 watts, which is the limit of 802.3af.
- Versatility: It caters to a broader range of devices, making it a versatile choice for modern applications.
Considerations:
- Cost: PoE+ infrastructure may be costlier than 802.3af, and devices supporting PoE+ may come at a higher price.
IEEE 802.3af (PoE)
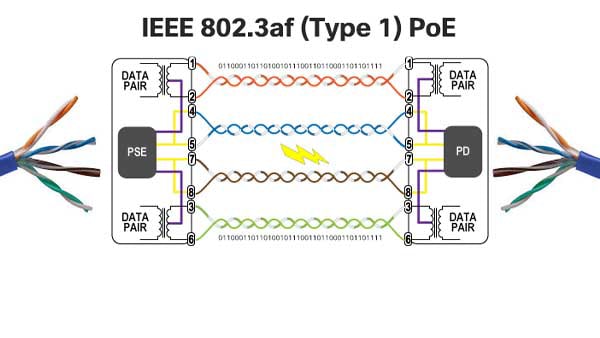
- Power Level: IEEE 802.3af is the original PoE standard, providing a power budget of up to 15.4 watts per port.
- Power Delivery: It is suitable for low to medium-power devices like basic IP cameras, VoIP phones, and access points.
- Applications: Commonly used for devices with modest power requirements.
Benefits:
- Cost-Effective: 802.3af infrastructure is generally more cost-effective than PoE+.
- Standard Devices: Many devices, especially older ones, are designed to work with 802.3af, ensuring compatibility.
Considerations:
- Power Limitation: Devices requiring more than 15.4 watts may not be adequately powered using 802.3af.
Choosing Between 802.3at and 802.3af
Factors to Consider:
- Device Power Requirements: Assess the wattage needs of devices; choose 802.3at for higher demands.
- Cost Considerations: Evaluate the budget for infrastructure and power-related expenses.
- Device Compatibility: Ensure devices align with the chosen standard.
The decision between 802.3at and 802.3af hinges on understanding the power needs of devices and balancing cost considerations. While 802.3af remains a cost-effective solution for devices with modest power needs, 802.3at accommodates a broader range, albeit potentially at a higher cost. It's a matter of aligning standards with your network's unique requirements.
Beyond Today: What Lies Ahead in PoE Standards?
As technology advances, standards like 802.3bt (Type 3 and Type 4) are emerging to cater to increased power demands. Upgrading switching gear becomes crucial to support the latest devices efficiently.
Fully IEEE802.3AF Compliant: PowerBx's Commitment
PowerBx's PoE devices proudly adhere to the IEEE 802.3af standard, ensuring compatibility and reliability. The commitment to being Fully IEEE802.3AF Compliant speaks volumes about PowerBx's dedication to industry standards.
In the 802.3at vs. 802.3af dilemma, the key is aligning choices with specific network needs. Whether embracing the cost-effectiveness of 802.3af or the versatility of 802.3at, the aim is an efficient, future-ready network. Consider your devices' power appetites, budget constraints, and the ever-evolving landscape of PoE standards to make informed decisions.



